Practical Solutions for Protecting Healthcare Personnel
Healthcare Worker Safety is Fundamental to Patient Safety
Healthcare settings such as hospitals, clinics and laboratories are also high-risk work environments.
Healthcare personnel face numerous risks, ranging from infections and chemical exposure to psychological stress and musculoskeletal injuries.
Therefore, protecting healthcare workers is essential for the sustainability of healthcare services.
So, what can be done to improve healthcare worker safety? Here are practical and effective solutions that can be implemented at both the individual and organisational levels.
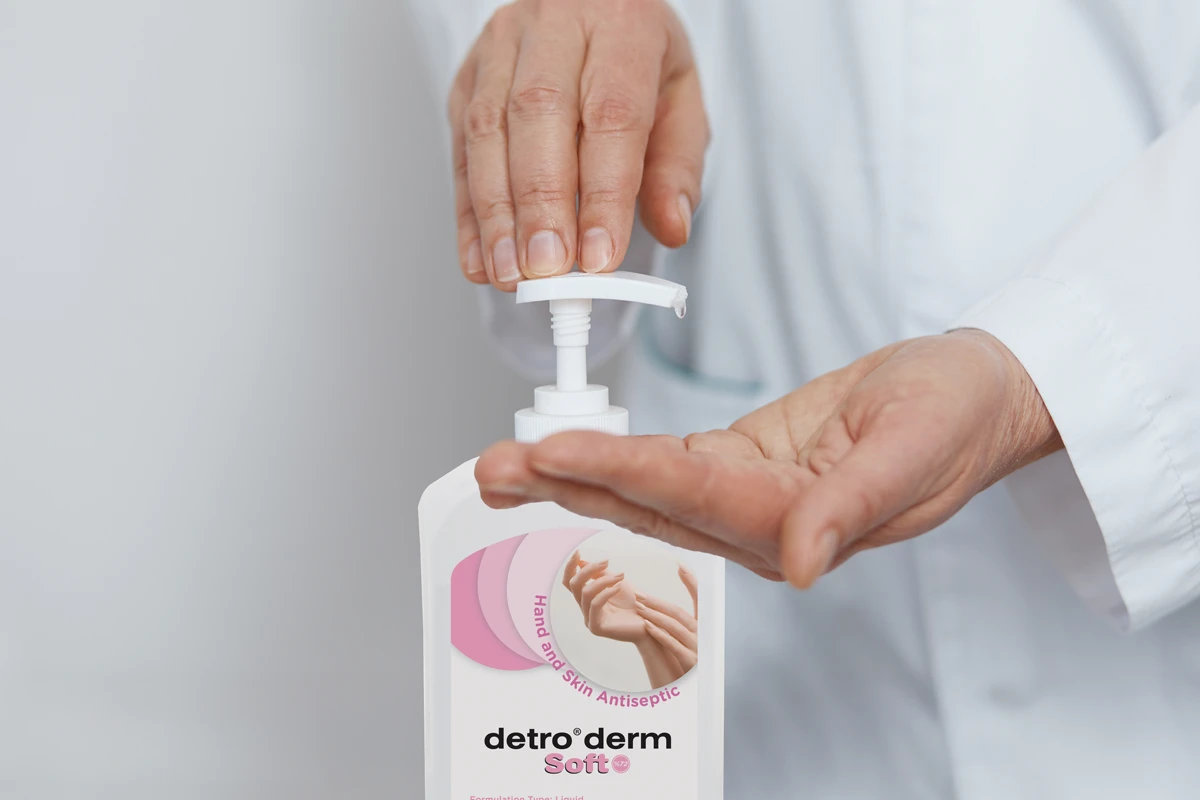
1. Hand Hygiene: The Simplest and Most Effective Protection Method
Hand hygiene is the first line of defence in breaking the chain of infection.
According to the World Health Organisation, proper hand antisepsis can prevent more than 50% of infections.
Practical recommendations:
- Hands should be disinfected with antiseptic before and after each patient contact.
- Alcohol-based hand antiseptics should be used when soap and water are not available.
- Antiseptics containing moisturisers should be preferred to prevent skin irritation.
- Factors such as jewellery, rings, or long nails increase the retention of microorganisms and make hand hygiene more difficult.
💡 Remember: Effective hand hygiene protects not only the patient but also the healthcare worker.
2. Correct Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
The correct and regular use of protective equipment such as masks, gloves, gowns, goggles, and face shields is vital for protecting healthcare personnel.
Practical tips:
- Gloves are single-use and must be replaced with new ones when changing patients or procedures.
- Hands must be disinfected before putting on and after removing protective equipment.
- Proper disposal of PPE prevents cross-contamination.
3. Compliance with Infection Control Protocols
Every hospital or healthcare facility establishes specific protocols through infection control committees.
However, what is truly important in practice is the active implementation of these protocols in the field.
Actions that can be taken at the institutional level:
- Hand hygiene, surface disinfection and waste management processes should be regularly monitored.
- Healthcare personnel should receive infection control training at least once a year.
- Effective surface disinfectants should be used for high-touch surfaces (door handles, monitors, keyboards, etc.) in clinics.
4. Protection Against Chemical Exposure
Healthcare personnel may be exposed to substances such as biocidal products, detergents, or sterilisation chemicals, particularly in laboratories and disinfection units.
Practical solutions:
- Products bearing a biocidal authorisation number on their labels should be preferred, while disinfectants covered by medical device regulations should bear the CE mark and the relevant approved body number.
- Work should be carried out in areas with a powerful ventilation system; chemical mixtures should not be prepared in enclosed spaces.
- Respiratory protection and goggles should be used when necessary.
💬 Remember: The right product, the right dose, and the right duration are the keys to safe disinfection.
5. Awareness of Psychosocial Risks
Long shifts, high workloads, and constant stress can lead to burnout syndrome among healthcare workers.
Mental resilience is as fundamental to occupational sustainability as physical safety.
Recommendations:
- Regular breaks should be provided at set intervals.
- A supportive communication culture should be fostered among staff.
- Organisations should provide psychological support mechanisms (e.g. counselling services) to their staff.
6. Protecting Skin Health
The intensive use of disinfectants can cause problems such as dryness, cracking and dermatitis in the hands.
This creates a breeding ground for infections.
Skin protection recommendations:
- Antiseptics with moisturising formulations should be used.
- Hands should be moisturised.
- Irritated areas should be treated promptly.
7. Continuity of Equipment and Surface Hygiene
Equipment used by healthcare personnel, such as stethoscopes, blood pressure monitors, monitors or computers, can also be part of the chain of infection.
Therefore, regular surface disinfection is fundamental to both personal and environmental protection.
Practical solution:
- Single-use disinfectant wipes containing alcohol or chlorhexidine should be used.
- Device surfaces should be wiped down after each use.
- Products that prevent biofilm formation should be preferred, especially in intensive care and emergency departments.
8. Vaccinations and Periodic Health Checks
Maintaining a strong immune system among healthcare personnel is one of the most effective defences against infection risk.
- Hepatitis B, influenza, and tetanus vaccinations should be administered regularly.
- Annual health checks are important for the early detection of occupational exposures.
Health Worker Safety is the Guarantee of Public Health
The quality of healthcare services is directly related to how well healthcare personnel are protected.
Proper hygiene habits, appropriate product selection, personal protective measures, and institutional support mechanisms ensure that employees remain physically and psychologically strong.
Let us not forget: Protecting healthcare personnel is not just an individual measure — it is the guarantee of public health.